Do you often feel fatigued, have a headache, or experience dry skin? These could be signs that you’re not properly hydrated. Dehydration is a common issue that many people overlook, but it can have serious consequences on your health if left untreated.
Hydration is essential for our bodies to function properly. However, many of us do not drink enough water throughout the day, leading to dehydration. It’s important to be aware of the signs of dehydration so that you can take action to stay properly hydrated.
In this article, we will discuss the signs of dehydration that you should be on the lookout for. By understanding these signs, you can take the necessary steps to ensure you are drinking enough water and staying properly hydrated for overall health and well-being.
Causes of Dehydration
Dehydration occurs when the body loses more fluids than it takes in. There are several causes of dehydration that individuals should be aware of in order to prevent and manage this condition effectively.
The first cause of dehydration is inadequate fluid intake. Many people simply do not drink enough water or fluids throughout the day, leading to a depletion of body fluids. It is essential to consume an adequate amount of fluids, especially during hot weather or when engaging in physical activity.
Excessive sweating is another common cause of dehydration. When the body sweats excessively, it loses vital fluids that need to be replenished promptly. This is particularly important for athletes or individuals who spend a significant amount of time in hot and humid environments.
Certain illnesses or medical conditions can also contribute to dehydration. Fever, vomiting, and diarrhea can cause the body to lose fluids rapidly, leading to dehydration. It is vital to seek medical attention promptly when experiencing these symptoms, as they can exacerbate dehydration if left untreated.
Moreover, some medications can increase urination, leading to fluid loss. Diuretics, often prescribed for high blood pressure or heart conditions, are known to enhance urine production. It is crucial for individuals taking these medications to monitor their fluid intake carefully to prevent dehydration.
Common Signs of Dehydration
Dehydration occurs when the body lacks an adequate amount of water to function properly. It can happen due to various reasons such as excessive sweating, vomiting, diarrhea, or simply not consuming enough fluids. Recognizing the signs of dehydration is crucial in order to prevent further complications.
One of the most common symptoms of dehydration is thirst. When the body is dehydrated, it sends signals to the brain to increase fluid intake. Additionally, dark yellow urine is often indicative of dehydration. Normally, urine is pale yellow or clear, so when it becomes dark yellow, it suggests that the body is not adequately hydrated.
Dry mouth and skin are also common signs of dehydration. When there is a lack of water in the body, saliva production decreases, leading to a dry mouth. The skin may also become dry and less elastic, as water is essential for maintaining healthy skin.
Fatigue and lightheadedness are other noticeable symptoms of dehydration. When the body is dehydrated, it becomes more difficult for the heart to pump blood efficiently, resulting in a drop in blood pressure. This can lead to feelings of weakness, fatigue, and dizziness.
Headaches and muscle cramps are common complaints for individuals who are dehydrated. The brain is sensitive to the lack of water, and this can cause headaches. Additionally, muscles need adequate hydration to function properly. Lack of fluids can lead to muscle cramps and discomfort.
Another sign of dehydration is decreased urine output. The body tries to conserve water when it is dehydrated, so the kidneys produce less urine. This can also contribute to the darker color of urine.
Severe Signs of Dehydration
Severe dehydration can have a significant impact on the body and should be taken seriously. It is important to recognize the signs of severe dehydration so that prompt medical attention can be sought.
One of the key indicators of severe dehydration is a rapid heartbeat. When the body is dehydrated, the volume of blood circulating decreases, causing the heart to work harder to pump blood to the organs and tissues. This can lead to an increased heart rate and palpitations.
Another sign of severe dehydration is sunken eyes. Dehydration causes a reduction in the body’s fluid levels, including the fluid around the eyes. As a result, the eyes may appear sunken and dull.
Confusion or irritability is also a common symptom of severe dehydration. When the body lacks adequate fluids, it can negatively impact brain function, leading to confusion, difficulty concentrating, and even mood changes, such as irritability.
Rapid breathing is another sign to watch out for. Dehydration can cause a decrease in blood volume, leading to a decrease in oxygen delivery to the body’s organs and tissues. In response, the body may increase the respiratory rate to compensate for the lack of oxygen, resulting in rapid and shallow breathing.
Fainting is a severe sign of dehydration that should not be ignored. When the body is severely dehydrated, it struggles to maintain adequate blood flow to the brain. This can result in a sudden loss of consciousness or fainting.
Lastly, low blood pressure is a critical indicator of severe dehydration. Dehydration can cause a decrease in blood volume, leading to low blood pressure. This can result in dizziness, lightheadedness, and even shock if left untreated.
Recognizing and responding quickly to these signs of severe dehydration is crucial. If you or someone you know experiences these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Rehydration therapy, such as intravenous fluids, may be necessary to restore hydration levels and prevent any further complications.
Effects of Dehydration on the Body
Dehydration is a condition that occurs when the body does not have enough water to function properly. This can have detrimental effects on various aspects of our body, including physical performance and cognitive function.
One of the immediate impacts of dehydration is on physical performance. When we are dehydrated, our muscles become fatigued more easily and our endurance decreases. This can result in decreased strength, speed, and overall athletic performance. Additionally, dehydration affects the body’s ability to regulate its temperature, making it more difficult to cool down during exercise and increasing the risk of heat-related illnesses, such as heat exhaustion or heat stroke.
In terms of cognitive function, dehydration can impair our ability to think clearly, concentrate, and make decisions. Studies have shown that even mild dehydration can negatively affect our mood, memory, and mental performance. This can have serious consequences, especially in situations where focus and alertness are crucial, such as driving or operating machinery.
Dehydration can also lead to kidney and urinary problems. When we don’t have enough water in our system, it becomes harder for our kidneys to remove waste and toxins from our blood. This can increase the risk of kidney stones, urinary tract infections, and other urinary issues.
Certain groups, such as the elderly and infants, are more susceptible to the complications of dehydration. Older adults may have a diminished sense of thirst, making it harder for them to recognize when they need to drink water. Infants, on the other hand, have a higher water requirement per pound of body weight and are at a greater risk of becoming dehydrated.
Prevention and Treatment of Dehydration
Dehydration occurs when the body loses more water than it takes in. It can lead to various complications, ranging from mild symptoms like dry mouth and fatigue to severe conditions like dizziness, rapid heartbeat, and even organ failure. To prevent and treat dehydration, it is crucial to implement some effective measures.
Increasing fluid intake is the first step to preventing dehydration. Drinking an adequate amount of water throughout the day helps replenish the body’s water levels. Additionally, consuming water-rich foods like fruits and vegetables can contribute to hydration. Such foods include watermelon, cucumbers, strawberries, and lettuce.
Avoiding excessive alcohol and caffeine consumption is another crucial factor in preventing dehydration. Both alcohol and caffeine act as diuretics, increasing urine production and thereby further depleting the body of water.
Recognizing and addressing signs of dehydration promptly is essential. Symptoms can vary from mild to severe, so monitoring the body’s hydration levels is crucial. If any signs of dehydration are noticed, such as increased thirst, dark urine, or dry skin, immediate action should be taken.
Hydration drink can be beneficial in preventing and treating dehydration. These drinks contain electrolytes, which help restore and maintain fluid balance in the body. They are especially useful during physical activities or in cases of mild dehydration.
In case of severe dehydration, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly. Severe dehydration is a medical emergency and may require intravenous fluids to rehydrate the body quickly and efficiently.
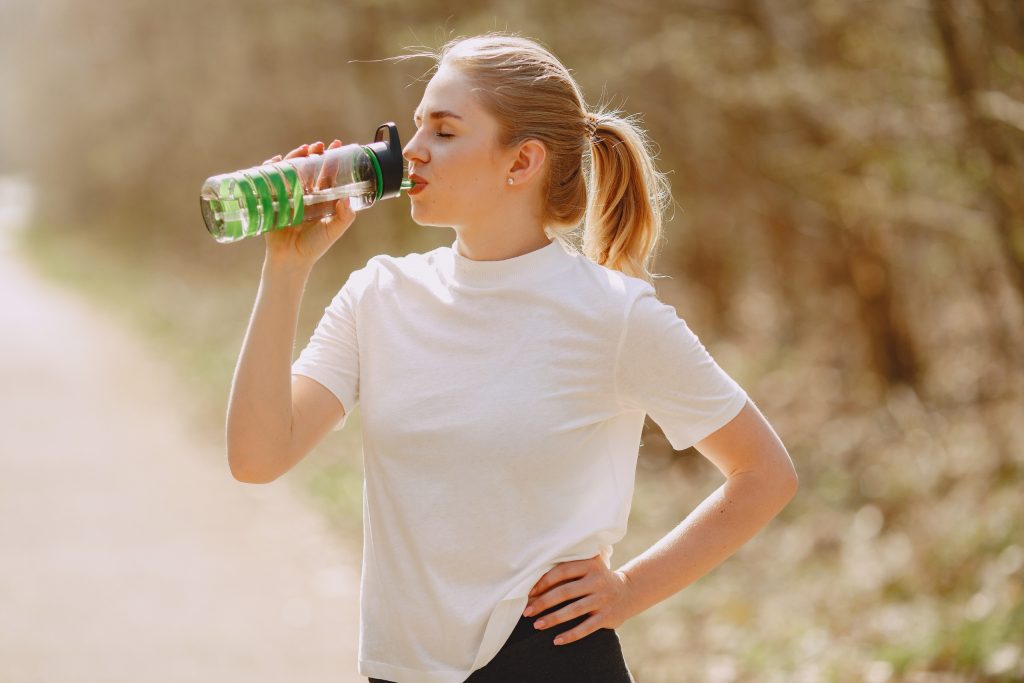

Conclusion
In conclusion, staying hydrated is vital for our overall health and well-being. Dehydration can lead to numerous negative effects on our bodies, including dizziness, fatigue, dry skin, and even decreased cognitive function. To prevent dehydration, it is important to recognize the early signs, such as increased thirst, dry mouth, and dark urine. By drinking enough fluids throughout the day, including water and other hydrating beverages, we can ensure that our bodies stay properly hydrated. This can have a significant impact on our physical and mental health, as well as our ability to perform daily tasks and activities. So, let’s prioritize hydration and make it a habit to regularly consume fluids to keep our bodies functioning optimally!